【摘要】
视神经鞘具有特殊的解剖结构,颅内压增高时视神经鞘直径(optic nerve sheath diameter,ONSD)会出现增粗,故超声检查视神经鞘直径可以无创、床旁评估颅内压增高。国内外相关领域的研究对于诊断高颅压的ONSD的最佳临界值有差异,故我们建议在运用此技术评估颅内压增高时需要考虑种族差异,建立适合不同种族的诊断标准。超声检测ONSD具有广阔的应用和研究前景。
《超声评估中国健康成年人视神经鞘直径》
(Ultrasound Med Biol. 2016 Mar;42(3):683-8)
【摘要】
目的 确定中国正常成人视神经鞘直径(optic nerve sheath diameter,ONSD)的参考值范围,并且探索与其相关的影响因素。
方法 以2013年1月-2014年1月健康体检的成年人作为研究对象,每位受试者的双眼视神经鞘的矢状位和横断面均由两位医生分别测量两次。每位受试者ONSD的最终报告值是双眼视神经鞘的16个测量值的平均值。
结果 共有230例受试者,获得3680个ONSD测量值,ONSD平均值 为( 3.4580± 0.2767 )m m ,其 9 5 % 可 信 区 间 为 3.420~3.493 mm。ONSD的上限值低于以往白种人及黑人的研究结果。简单线性回归分析发现ONSD与性别、体质指数(body mass index,BMI)、腰围、头围相关。在调整了其他可能的影响因素后发现性别(偏回归系数0.189,P<0.001)、BM(I 偏回归系数0.032,P <0.001)是ONSD的独立影响因素。低体重组的女性ONSD最小。
结论 在确立ONSD的正常值标准时应考虑种族、性别、BMI的差别。
《中国高颅压患者视神经鞘直径的诊断价值》
(PLoS One,2015,10(2):e0117939-e0117939)
【Abstract】
目的 确定视神经鞘直径(optic n erve s heath d iameter,ONSD)评估颅内压(intracranial p ressure,ICP)增高的诊断标准并研究其相关影响因素。
方法 本研究为双盲横断面研究,收集2013年3月-12月可疑高ICP需要进行腰椎穿刺测量脑脊液压力的患者为研究对象,记录患者的个体相关信息及脑脊液压力值,分为ICP正常组及增高组,比较两组患者相关因素的差异。运用接受者操作特性曲线(receiver operating characteristic,ROC)确定高ICP的ONSD最佳诊断值。
结果 共收录了279例患者,其中包括101例高ICP患者。比较显示,ONSD是ICP的独立预测因素(P<0.001),不受性别、年龄、体质指数(body mass index,BMI)、头围、腰围、高血压和病因分型的影响。ONSD能够有效准确地评估高ICP。运用超声检测ONSD诊断高ICP的最佳临界值是4.1 mm(敏感度95%,特异度92%)。
结论 我国高ICP患者的ONSD的诊断值比白种人低,因此建议检测ONSD评估高ICP时应该注意种族差异。
We aimed to quantitatively assess intracranial pressure (ICP) using optic nerve sheath diameter (ONSD)measurements. We recruited 316 neurology patients in whom ultrasonographic ONSD was measured before lumbar puncture. They were randomly divided into a modeling and a test group at a ratio of 7:3. In the modeling group, we conducted univariate and multivariate analyses to assess associations between ICP and ONSD, age, sex, BMI, mean arterial blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure. We derived the mathematical function “Xing & Wang” from the modelling group to predict ICP and evaluated the function in the test group. In the modeling group, ICP was strongly correlated with ONSD (r = 0.758, p < 0.001), and this association was independent of other factors. The mathematical function was ICP = −111.92 + 77.36 × ONSD (Durbin-Watson value = 1.94). In the test group, a significant correlation was found between the observed and predicted ICP (r = 0.76, p < 0.001). Bland-Altman analysis yielded a mean difference between measurements of −0.07 ± 41.55 mmH2O. The intraclass correlation coefficient and its 95%CIs for noninvasive ICP assessments using our prediction model was 0.86 (0.79–0.90). Ultrasonographic ONSD measurements provide a potential noninvasive method to quantify ICP that can be conducted at the bedside.
【作者注:建立并验证数学模型,通过视神经鞘检测,可定量评估高颅压】
《超声检测视神经鞘直径无创、动态评估颅内压》
(JAMA Ophthalmol. 2018 Mar 1;136(3):250-256)
背景及目的:有创性的颅内压(intracranialpressure, ICP)监测可导致多种并发症。因此临床急需无创、可重复性的评估ICP的方法,近些年超声检查视神经鞘直径(opticnerve sheath diameter, ONSD)评估ICP成为研究热点,我们证实了这种无创性技术可有效地诊断高ICP,然而该技术是否可动态监测ICP变化以及评估高ICP治疗效果尚不清楚。因此,本研究将探讨超声检测ONSD能否有效动态评估ICP的变化。
方法:研究对象为2015年8月1日到2015年10月31日在我院神经内科就诊,可疑高ICP需进行腰椎穿刺的患者,在腰椎穿刺之前由2名经验丰富的超声医生进行ONSD检测,运用Philips超声系统9-3MHz线阵探头轻柔地置于患者闭合的眼睑上,进行横断面及矢状面扫查,保存双侧视神经鞘清晰的图像。于球后3mm处测量ONSD,每个扫查方向测量两次。根据ICP结果患者被随机分为2组:第1组(200<ICP≤300mmH2O),第2组(ICP> 300 mmH2O)。高ICP的患者进行常规治疗,我们在1个月内复查患者的ONSD和ICP,分析入院时ONSD和ICP之间的相关性,比较治疗前后ONSD以及ICP的变化情况,分析△ONSD和△ICP之间的相关性,(△ONSD和△ICP是治疗前后ONSD和ICP的变化值)。
结果:我们共收集了60例患者(37例高ICP患者),入院时ICP与ONSD密切相关(r= 0.798,P<0.001)。其中25例高ICP患者(平均年龄35.16±12.4岁;男性13例)完成了随访。治疗前后ONSD存在显著性差异(P<0.001)。△ICP和△ONSD的均值分别为126.64±52.51mmH2O(范围:20~210mmH2O)和1.0±0.512mm(范围:0.418~ 2.37 mm)。△ONSD与△ICP呈正相关(r=0.702,P<0.001)。两组患者治疗后ICP及ONSD均恢复至正常范围,且两组患者ONSD的均值无显著性差异。
结论:超声检测ONSD可无创、简便、动态评估ICP变化及评估高ICP的治疗效果。
《Ultrasonic measurement of optic nerve sheath diameter:a non-invasive surrogate approach for dynamic,real-time evaluation of intracranial pressure》
(The British journal of ophthalmology. Apr 2019;103:437-441)
【Abstract】
The current study aimed to identify whether ultrasonographic measurements of optic nerve sheath diameter (ONSD) could dynamically and sensitively evaluate real-time intracranial pressure (ICP). ONSD
measurements were performed approximately 5 min prior to and after a lumbar puncture (LP). A total of 84 patients (mean±SD age, 43.5±14.7 years; 41 (49%) men; 18 patients with elevated ICP) were included in the study. The Spearman correlation coefficients between the two observers were 0.779 and 0.703 in the transverse section and 0.751 and 0.788 in the vertical section for the left and right eyes, respectively. The median (IQR) change in ONSD (ΔONSD) and change in ICP (ΔICP) were 0.11 (0.05–0.21) mm and 30 (20–40) mmH2O, respectively, for all participants. With a reduction in cerebrospinal fluid pressure, 80 subjects (95%) showed an immediate drop in ONSD; the median (IQR) decreased from 4.13 (4.02–4.38) mm to 4.02 (3.90–4.23) mm (p<0.001). Significant correlations were found between ONSD and ICP before LPs (r=0.482, p<0.01) and between ΔONSD and ΔICP (r=0.451, p<0.01). Ultrasonic measurement of ONSD can reflect the relative real-time changes in ICP.【The ONSD was measured with the Delica MVU-6300 (Shenzhen, Guangzhou, China),】
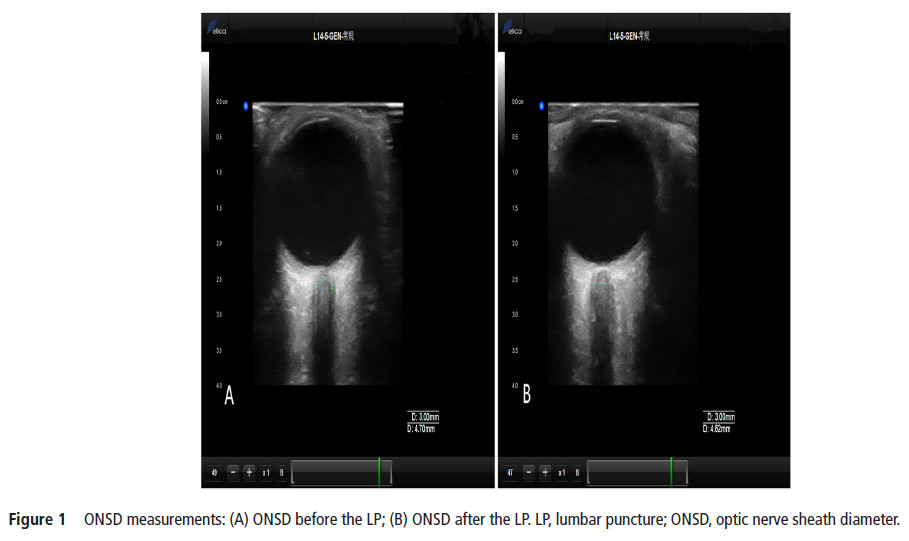
【作者注:腰穿前后对比视神经鞘变化,发现超声检测视神经鞘直径可以实时显示颅内压改变,也进一步证实了关于视神经鞘研究的规范操作流程,应该在腰穿之前进行视神经鞘测量】。
《 Reliability of Assessing Non-severe Elevation of Intracranial Pressure Using Optic NerveSheath Diameter and Transcranial Doppler Parameters》
(Frontiers in Neurology.2019.Oct 22;10)
Background/Aims: Non-invasive measurement of intracranial pressure (ICP) usingultrasound has garnered increasing attention. This study aimed to compare the reliability of ultrasonographic measurement of optic nerve sheath diameter (ONSD) and transcranial Doppler (TCD) in detecting potential ICP elevations.
【Delica MVU-6300 (Shenzhen, Guangdong, China) was used to obtain both TCD and ONSD measurements】
Methods: Patients who needed lumbar puncture (LP) in the Department of Neurology were recruited from December 2016 to July 2017. The ONSD and TCD measurements were completed before LP.
Results: One hundred sixty-five participants (mean age, 41.96 ± 14.64 years; 80 men; 29 patients with elevated ICP) were included in this study. The mean ICP was 170 ± 52 mmH2O (range, 75–400 mmH2O). Univariate analyses revealed that ICP was non-significantly associated with TCD parameters and significantly associated with ONSD (r = 0.60, P < 0.001). The mean ONSD of the elevated ICP group was significantly higher than that of the normal ICP group (4.53 ± 0.40mm vs. 3.97 ± 0.23mm; P < 0.001). Multivariate linear regression determined that the difference between ICP and ONSD is significant.

Conclusions: In the early stage of intracranial hypertension, ONSD is more reliable for evaluating ICP than TCD.
《The prevalence of intracranial stenosis in patients at low and moderate risk of stroke 》
(Ther Adv Neurol Disord.2019,Vol.12: 1–11)
【Abstract】
Background: Previous studies assessing the risk of stroke in the general population performed screening with Doppler ultrasonography only for high-risk patients and neglected low- and moderate-risk patients. The aims of this study were to explore the current prevalence of intracranial arterial stenosis (ICAS) and analyze its association with different levels of stroke risk and risk factors based on the risk assessment scale for stroke used inChina.
Methods: A total of 3654 participants who underwent transcranial Doppler ultrasound (TCD)【Delica EMS-9PB (Shenzhen, Guangdong, China)】were eligible for inclusion. Information regarding demographic characteristics and risk factors such as alcohol consumption and hypertension was collected through interviews and questionnaires and used to analyze the association of ICAS with different levels of stroke risk
and risk factors.
Results: The mean age of 501 subjects diagnosed with at least one ICAS was higher than that of participants without ICAS (57.13 ± 9.56 years and 55.52 ± 9.35 years, respectively). After adjusting for confounding factors, gender, education, residence, hypertension and personal history of stroke were associated with ICAS. The odds ratios for ICAS in patients with hypertension and a personal history of stroke were 1.655 [95% confidence interval (CI):1.341–2.043] and 1.854 (95% CI: 1.371–2.508), respectively. In addition, participants in the lowand moderate-risk stroke groups accounted for an unexpectedly high proportion of individuals with ICAS (up to 38.3%). Results from multivariate analyses indicated that the adjusted odds ratios for ICAS in patients with moderate and high stroke risks versus those with a low stroke risk were 1.603 (95% CI: 1.171–2.195) and 1.612 (95% CI: 1.272–2.042), respectively.
Conclusion: The prevalence of ICAS is high in northeast China and increases with the level of stroke risk. However, the proportion of patients with ICAS among those with low and moderate stroke risks should also be noted.
【作者注:对东北地区人群进行血管超声筛查。发现颅内血管狭窄患病率较高,且在颅内血管狭窄的人群中,中低危人群比例高达38.3%,故提示对于中低危人群血管筛查不容被忽视】。



